The current installation file in MSI format can be downloaded from the following URL:
Alternatively, this setup file is also available in a ZIP file:
The following parameters can be added to the setup and are used in these instructions:
/KEY - License key for agents (from our platform go.lywand.com)
/PROXY_URI - URI for specifying a proxy server (http://username:password@host:port)
/skipNetworkTest - Skips optional checks that require an internet connection
/forceInstall - Enables installation on unsupported operating systems. However, there is no guarantee of functionality
The installation parameters can also be specified using a configuration file. To do this, simply save a config.ini file in the same folder as lywand_setup.msi.
Example of a config.ini with license key and without proxy URI:
[General]
KEY=YOUR_LYWAND_AGENT_LICENSE_KEY
skipNetworkTest=false
forceInstall=false
[Proxy]
; e.g. http://username:password@host:port
PROXY_URI=
The preferred option is to roll out the agent using an existing software distribution system. An MSI package is available that can be installed with the following parameters:
MSI Command without Proxy
msiexec.exe /qn /i lywand_setup.msi WRAPPED_ARGUMENTS="/KEY=YOUR_LICENSE_KEY"
MSI Command with Proxy
msiexec.exe /qn /i lywand_setup.msi WRAPPED_ARGUMENTS=`"/KEY=YOUR_LICENSE_KEY /skipNetworkTest=true /PROXY_URI=http://USERNAME:PASSWORD@IP:PORT`"
The Windows-native method for distributing an application is to use Group Policy Objects (GPOs). In this case, the agent is configured via a separate config.ini file.
To ensure that all computers on which the agent is to be installed have access to the MSI file, a shared folder must be set up in the domain. This folder can be placed on the domain controller or a file server, for example.
1.1 Example with a shared folder on the C:/ disk on the domain controller:
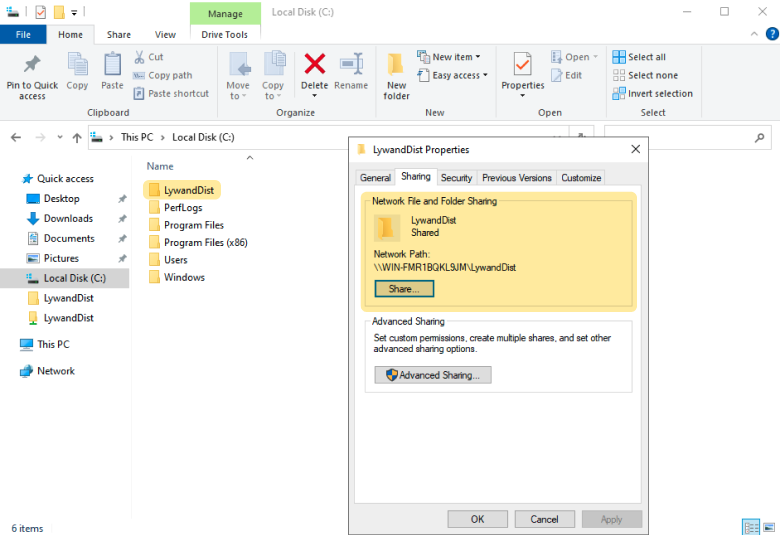
1.2 Create a configuration file
Create a config.ini that contains at least the license key.
[General]
KEY=YOUR_LYWAND_AGENT_LICENSE_KEY
skipNetworkTest=
[Proxy]
PROXY_URI=
1.3 Store Setup MSI and config.ini in this folder.
Now it is necessary to configure a GPO to perform the installation of the MSI package. The GPO should be placed in the Organizational Unit (OU) that contains the desired computers. Here, for example, in the domain controller OU:
2.1 Create GPO (if one does not yet exist)

2.2 Edit GPO
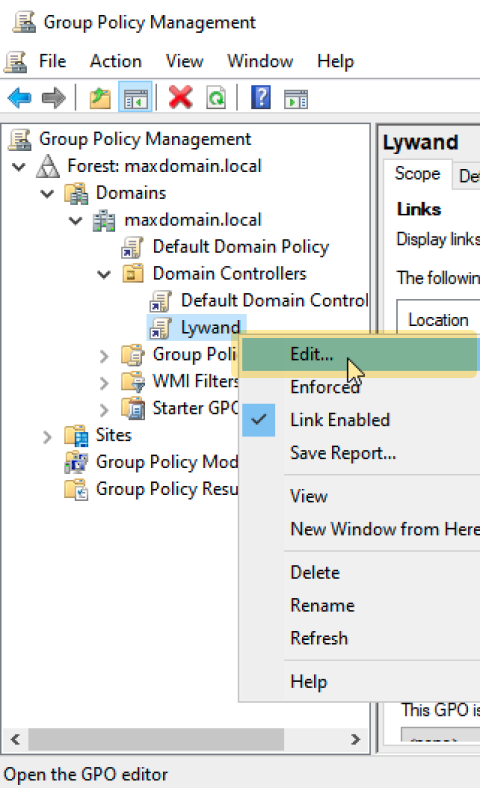
2.3 Add software package
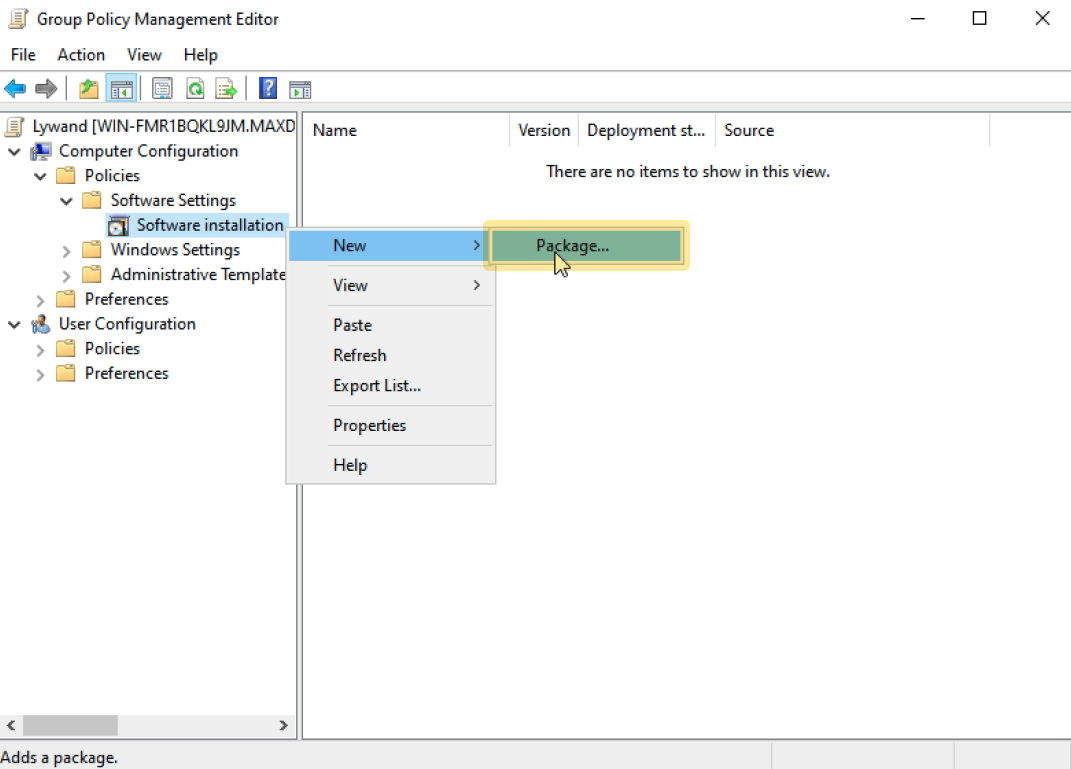
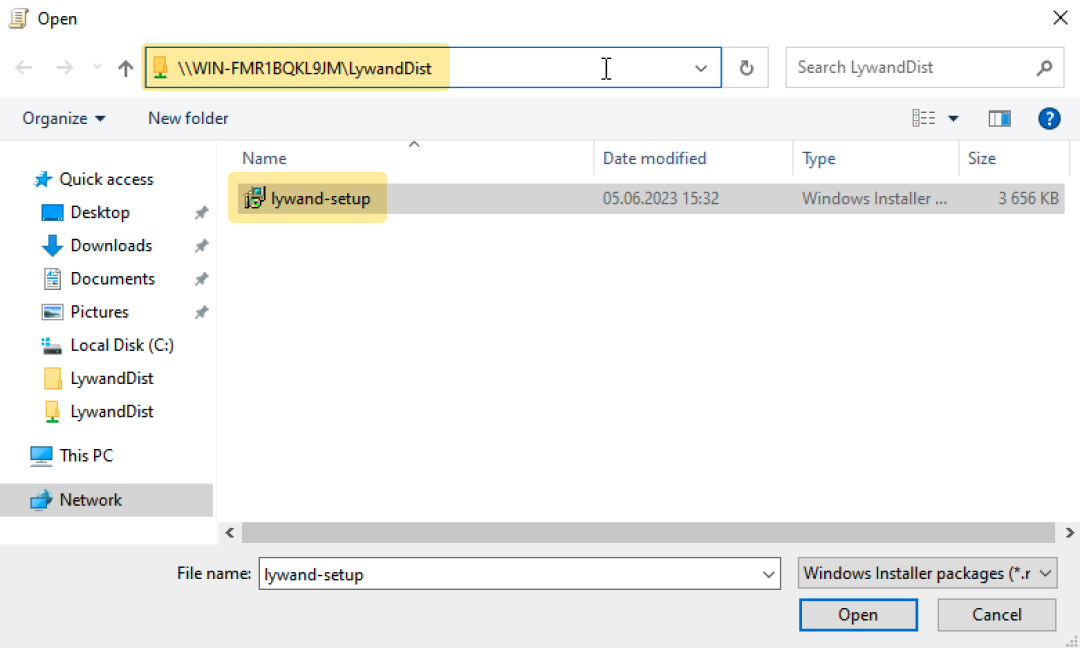
2.4 Select MSI
Important: Use the UNC path.
2.5 Update and check GPO
In Powershell, the GPO on a device can be updated with gpupdate /force.
You can then use gpresult /r to check whether the GPO is really applied to the device.
2.6 Restart computer
The agent should be successfully installed after the next computer restart.
Another option is to use the computer startup script GPO. This method installs the MSI file using a separate script that is executed when the computer is started.
To ensure that all computers on which the agent is to be installed have access to the MSI file and the script, it is necessary to set up a shared folder in the domain. This folder can be placed on the domain controller or a file server, for example.
Example with a shared folder on the C:/ disk on the domain controller:

Ideally, the script should be adapted to the specific infrastructure. The following example only serves as a simple template and must be adapted accordingly. At least the copy path and the license key must be replaced with your own values.
@ECHO OFF
rem Lywand
If exist "C:\Program Files (x86)\Lywand Agent\ly-service.exe" goto endeLywand
title Lywand installieren
copy \\WIN-8QEVHVGDTBL\LywandDist\lywand_setup.msi C:\lywand_setup.msi /Y
cd C:\
msiexec.exe /qn /i lywand_setup.msi WRAPPED_ARGUMENTS="/KEY=YOUR_LICENSE_KEY"
:endeLywandPowershell scripts can also be used in the GPO.
A GPO is now configured so that all desired computers execute the script at startup.
3.1 Create GPO (if one does not yet exist)

3.2 Edit GPO
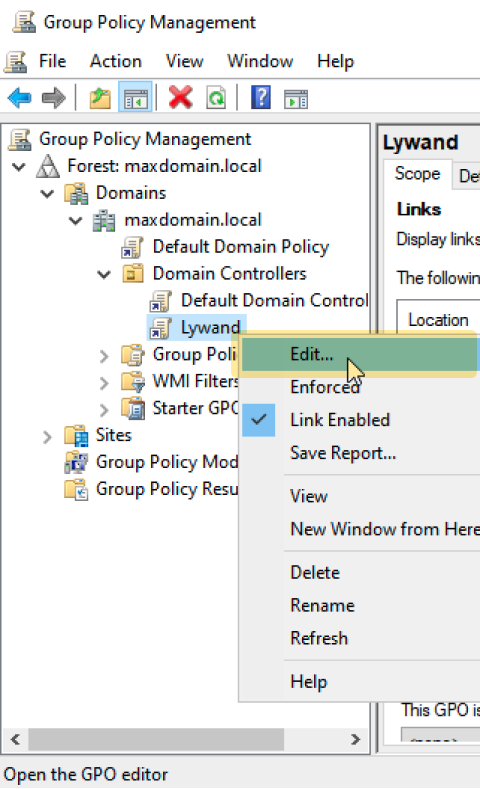
3.3 Configure start script
Important: Use the UNC path.
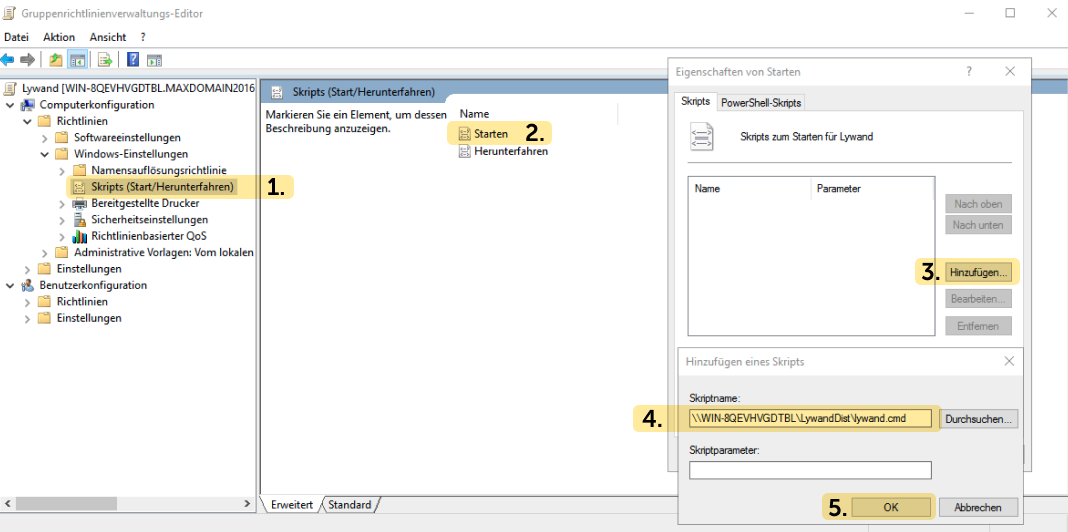
3.4 Update and check GPO
In Powershell, the GPO on a device can be updated with gpupdate /force.
You can then use gpresult /r to check whether the GPO is really applied to the device.
3.5 Restart computer
The agent should be successfully installed after the next computer restart.
In this variant, the MSI is installed via a scheduled task.
To ensure that all computers on which the agent is to be installed have access to the MSI file and the script, it is necessary to set up a shared folder in the domain. This folder can be placed on the domain controller or a file server, for example.
Example with a shared folder on the C:/ disk on the domain controller:
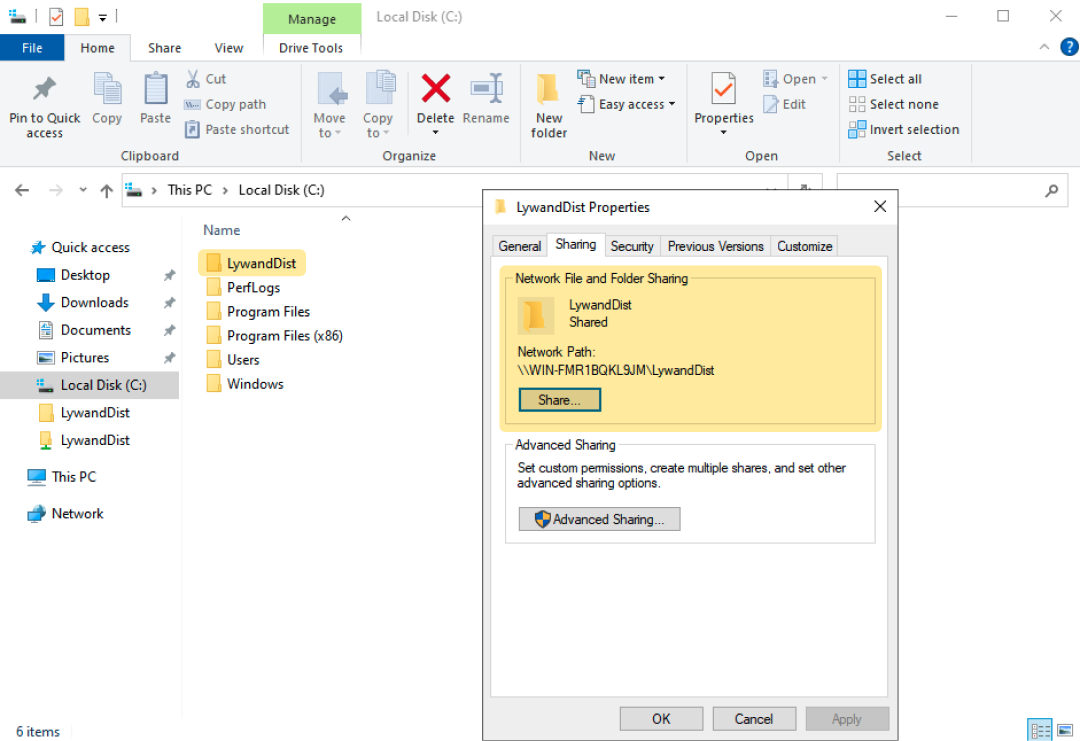
A GPO is now configured so that all desired computers receive the planned task.
2.1 Create GPO (if one does not yet exist)
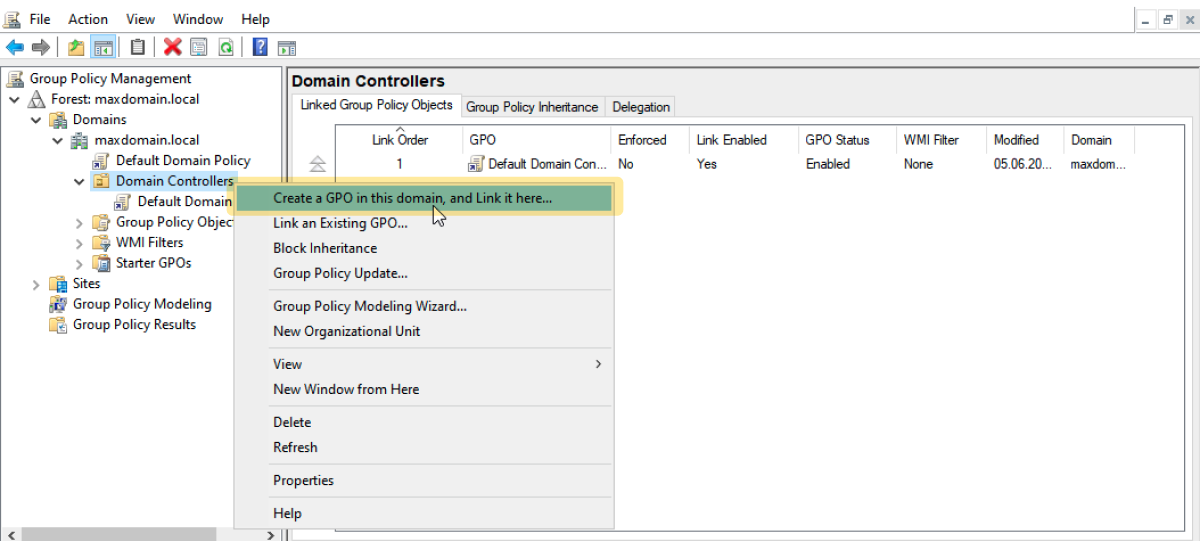
2.2 Edit GPO
2.3 General settings
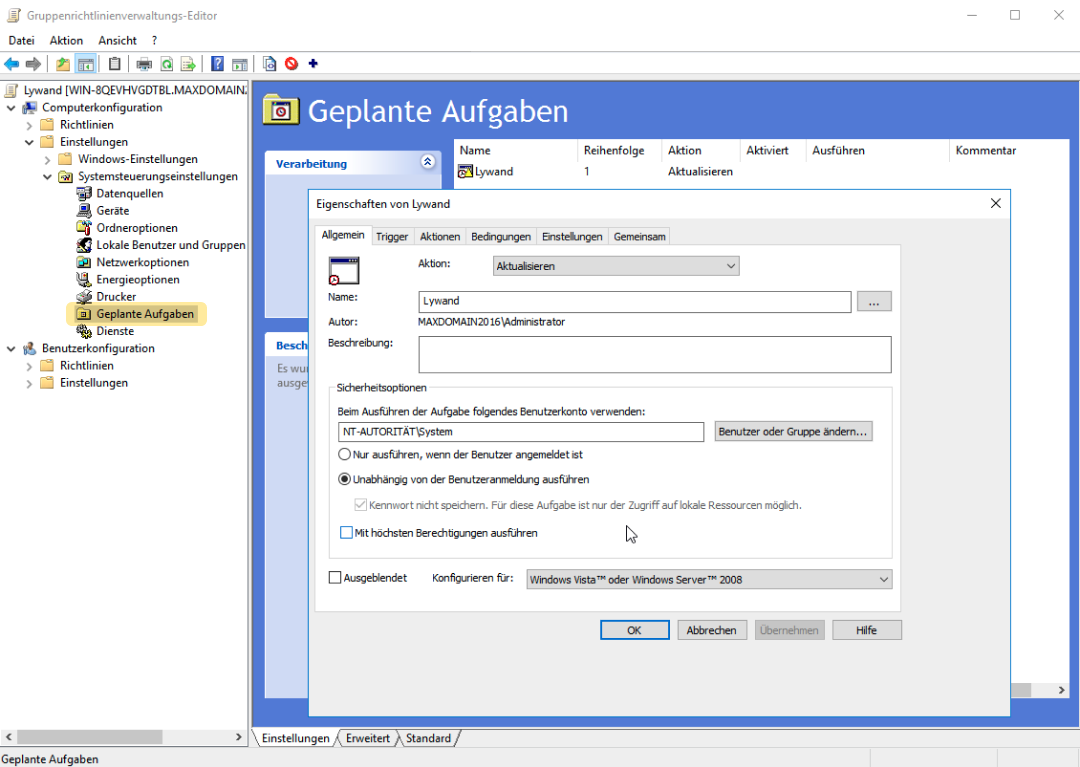
2.4 Set triggers
Please note that both triggers are required to ensure smooth operation of the startup:
At start
When creating/changing tasks
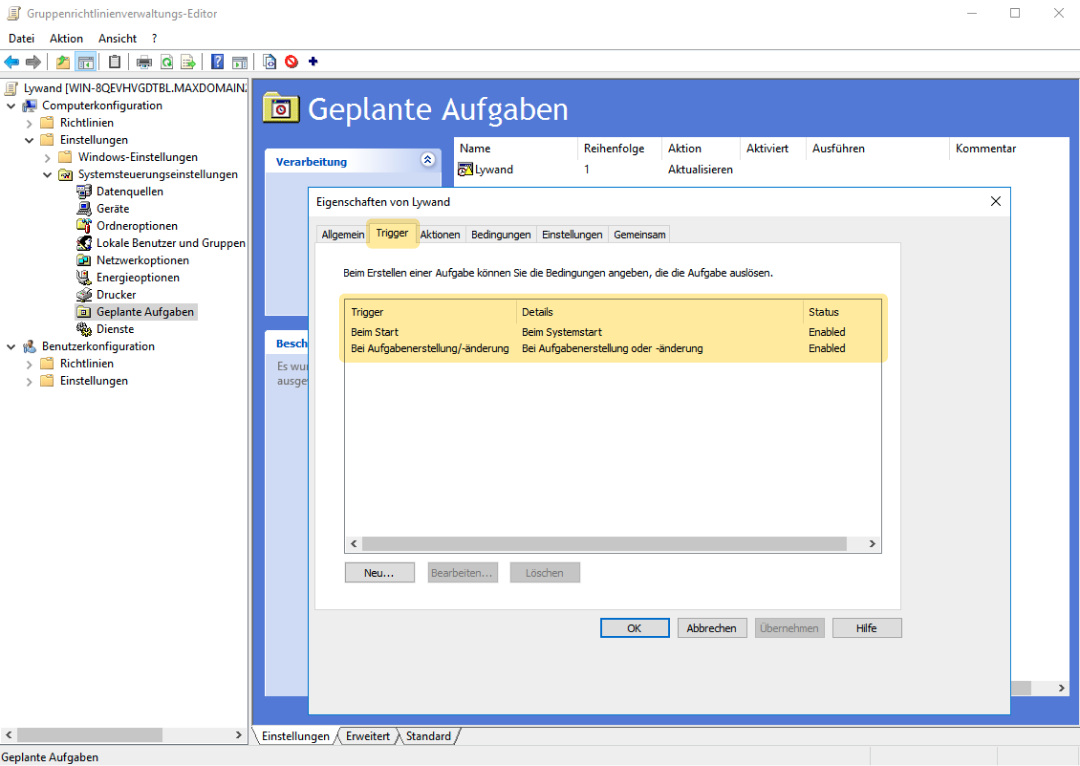
2.5 Fill command fields with your own license key and MSI path
Program = C:\Windows\System32\msiexec.exe
Argument without Proxy
/qn /i lywand_setup.msi WRAPPED_ARGUMENTS="/KEY=YOUR_LICENSE_KEY"
Argument with Proxy
/qn /i lywand_setup.msi WRAPPED_ARGUMENTS=`"/KEY=YOUR_LICENSE_KEY /skipNetworkTest=true /PROXY_URI=http://USERNAME:PASSWORD@IP:PORT`"
Start in = \\REMOTE_COMPUTER\MSI_PATH
2.6 Update and check GPO
In Powershell, the GPO on a device can be updated with gpupdate /force.
You can then use gpresult /r to check whether the GPO is really applied to the device.
2.7 Uninstall agent and restart
To test whether the task works on startup, the agent should first be uninstalled and a restart should be performed.
To do this, you can execute the following command in a CMD/PowerShell:
msiexec.exe /qn /x lywand_setup.msi
Same as option 2 but with an MST file instead of the simpler config.ini file. This option has been replaced by option 2.
To ensure that all computers on which the agent is to be installed have access to the MSI file, a shared folder must be set up in the domain. This folder can be placed on the domain controller or a file server, for example.
1.1 Example with a shared folder on the C:/ disk on the domain controller:

1.2 Store the Setup MSI in this folder.
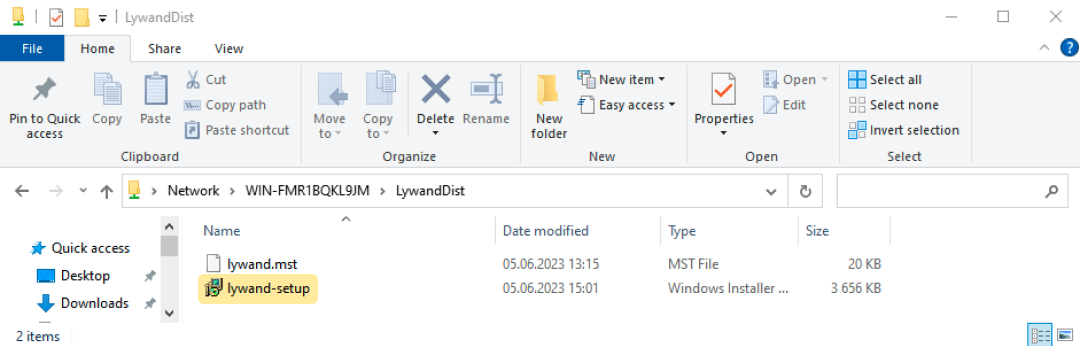
An MST file is required to link a license key to the MSI package. There are various programs for creating MST files, but Microsoft offers the "Orca" application for this purpose.
To download Orca, you can use the Windows SDK. Only the "MSI Tools" feature is required during installation.
2.1 Install Orca
After installing the Windows SDK, Orca must be installed separately under the following path (or a similar path):
C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\bin\10.0.22621.0\x86\Orca-x86_en-us.msi
2.2 Open MSI with Orca
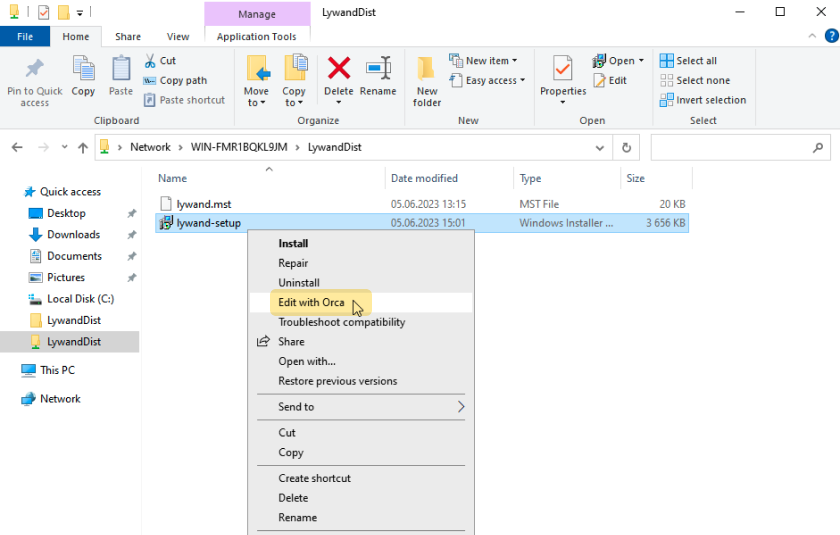
2.3 Create transform
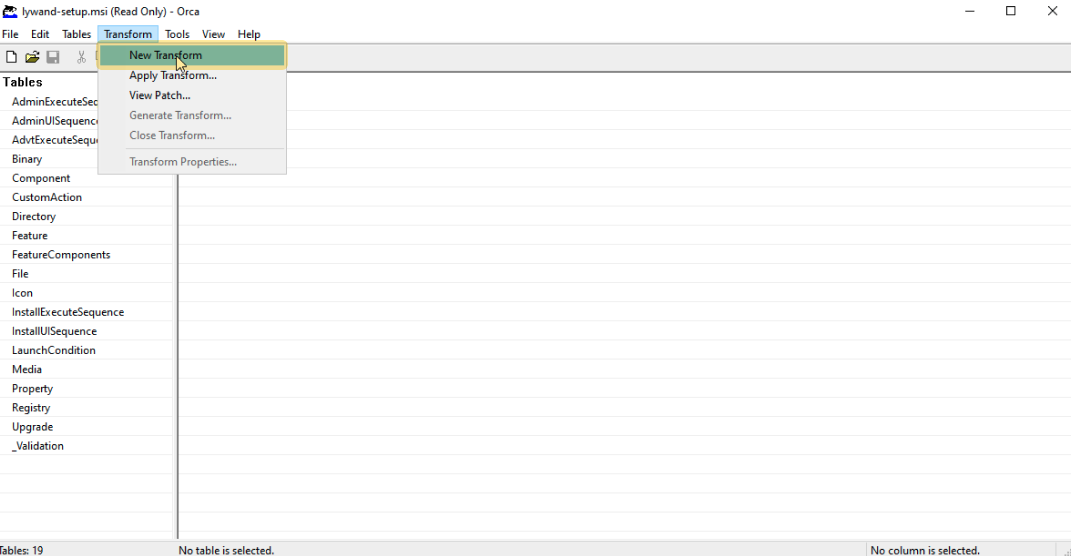
2.4 Add entry under property
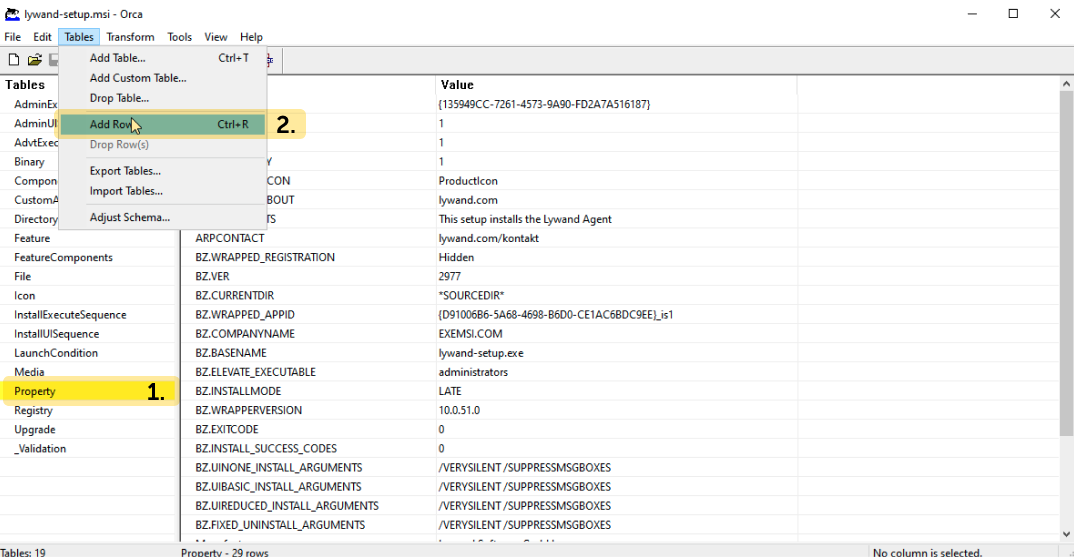
2.5 Inserting data
You still need to insert the license key here. You can find the license key in the infrastructure of the corresponding customer on go.lywand.com.
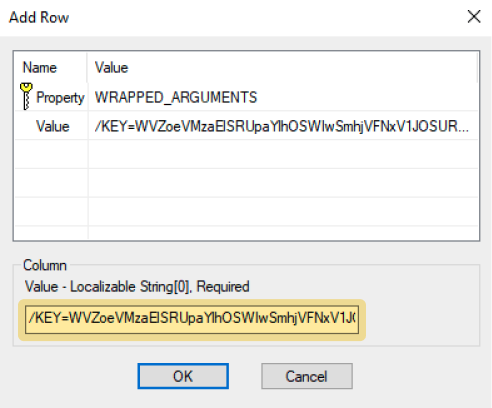
2.6 Generate and save transform (in the same folder as the MSI)
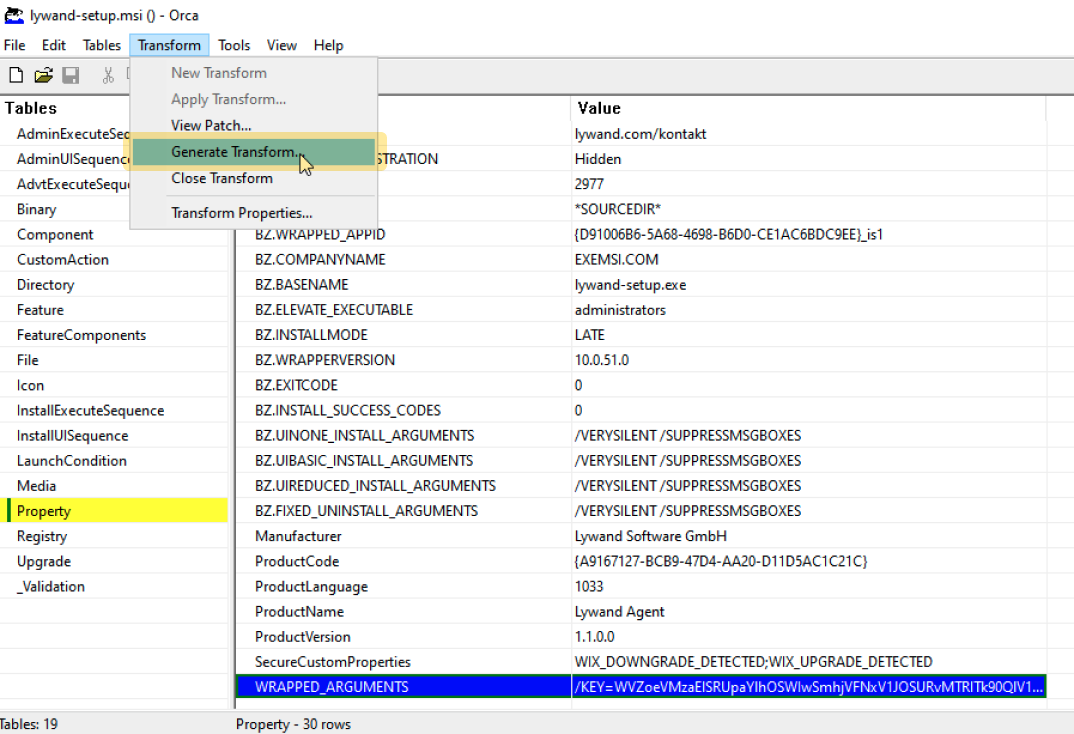
2.7 Close Orca
Orca must be closed, otherwise testing will not work.
After Orca has been closed, it is now necessary to configure a GPO to perform the installation of the MSI package. The GPO should be placed in the Organizational Unit (OU) that contains the desired computers. Here, for example, in the domain controller OU:
3.1 Create GPO (if one does not yet exist)

3.2 Edit GPO

3.3 Add software package

3.4 Select MSI
Important: Use the UNC path.

3.5 Select "Advanced"
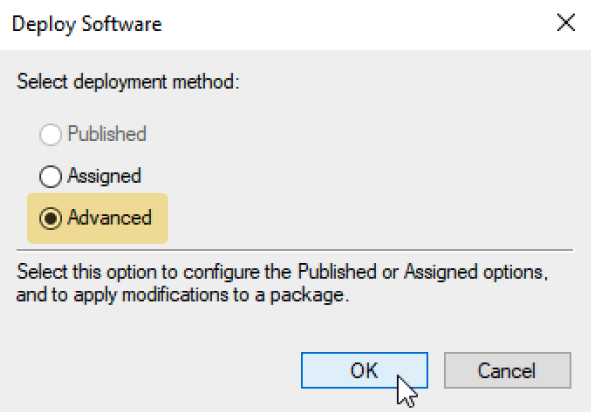
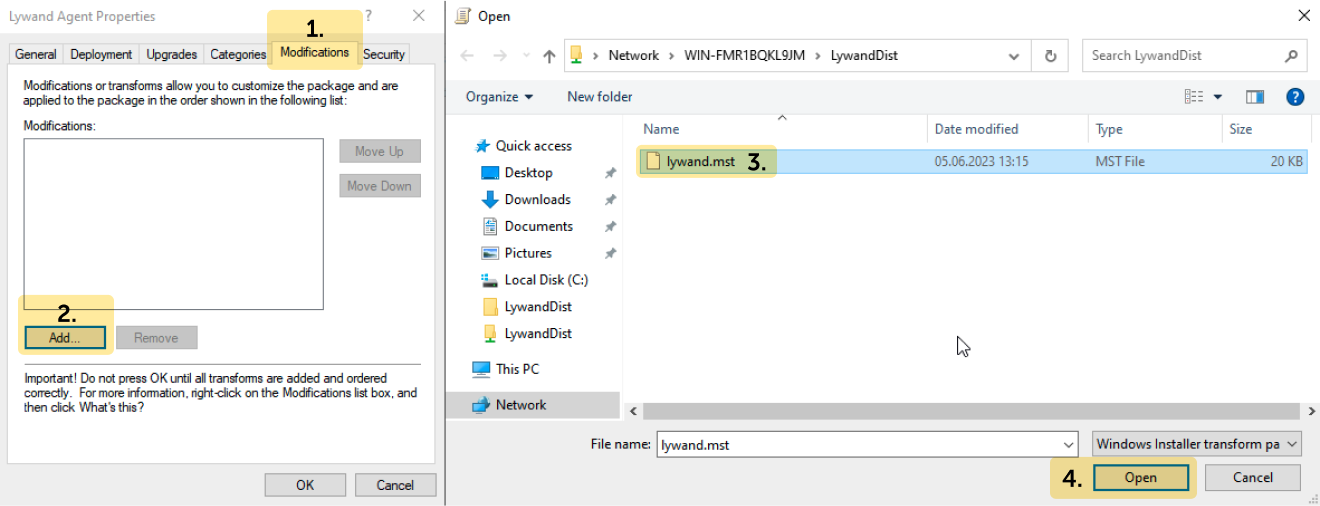
3.6 Add MST as a modification
3.7 Update and check GPO
In Powershell, the GPO on a device can be updated with gpupdate /force.
You can then use gpresult /r to check whether the GPO is really applied to the device.
3.8 Restart computer
The agent should be successfully installed after the next computer restart.
Make sure that the Group Policy (GPO) is linked in the correct organizational structure and that the desired computers are placed in this OU.
If it is necessary to clean up corrupt data (e.g. partially deleted data), please note the following points:
Remove the software from the GPO. (For option 1, also select the option to uninstall).
If the installation was not carried out via GPO or was not successful, uninstall the software manually via "Apps & Features".
Check on the device whether the agent has been completely uninstalled, including checking "Apps & Features", deleting program files, terminating services, etc. Also make sure that the GPO is configured correctly.
Make sure that the computers in the domain can access the remote share on which the MSI file is located. Check the permissions and adjust them if necessary.
The MST can also be tested without GPO with the following command in an Admin Powershell:
msiexec.exe /L*vx „C:\installerLog.txt“ /qn /i lywand_setup.msi TRANSFORMS=lywand.mstThe log file can be used to carry out a more detailed analysis of the error causes.